
Carrot
What is a Carrot?
Carrots are a long root vegetable with a fuzzy, grassy top. They are usually orange in color though white, purple, yellow, and red varieties of this vegetable are available. This vegetable is crunchy to eat, has an earthy and sweet flavor. It is eaten:
- Raw
- Grilled
- Boiled
- Steamed
- Fried
Carrots are one of the most popular vegetables worldwide. China produces the largest amount of this vegetable per year at 18,018,809 tons, followed by Uzbekistan, USA, Russian Federation, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Poland, Turkey, and Indonesia.
There are hundreds of different varieties of carrots, including:
- Deep Purple Hybrid
- Imperator 58
- Kaleidoscope
- Little Fingers
- Lunar White
- Parisian Heirloom
- Purple Dragon
- Red
- Short ‘n Sweet
- Solar Yellow
- Tendersweet
- Thumbelina
- Touchon
Origin of carrots
This vegetable was first domesticated for consumption in Central Asia (present day Iran) in the 10th century. These original root vegetables were purple and yellow in color. However, it is known that wild carrots were used in Afghanistan two hundred years before they began to be cultivated as a food crop. Going even further back, wild carrot seeds were found 5,000 years ago in Europe. It is likely that this vegetable may have been used by local populations then.
Arab expansion brought this vegetable both westwards and eastwards. The orange cultivar was developed in the 15th century in western Europe. This happened when a mutation occurred, removing the purple pigmentation from this vegetable, leading to the production of yellow carrots. The orange version of this vegetable developed from this breed.
Nutrition
This vegetable is highly nutritious, however, its nutrition levels vary with color. One carrot of medium size (61g) contains a nutritional value of:
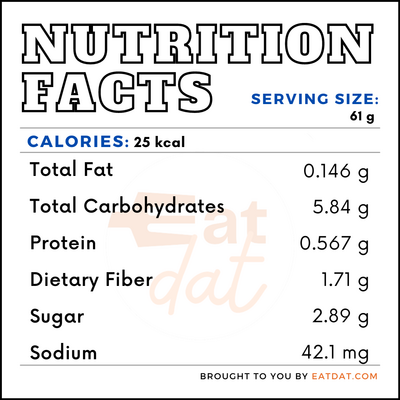
Orange carrots contain high levels of α and β-carotene, whereas the yellow variation provides lutein, red provides lycopene, and purple carrots provide anthocyanins. The black variation of this vegetable has high amounts of phenolic compounds. All these nutrients are beneficial for the human body. In addition, this vegetable also contains Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin K , Calcium, Iron, Potassium and Fiber.
Regular consumption of this vegetable can improve eyesight, lower the risk of cancer, reduce the risk of heart diseases, improve the immune system, and prevent constipation.
Commercial production
Growing carrots requires sandy loam soil, a dry and cool climate, and good irrigation. These vegetables are harvested when the roots appear at the surface. This vegetable is sold as fresh produce or processed in frozen, tinned, and pre-cooked forms. For best results, it should be washed, cleaned, and stored at 0°C.
Carrot recipes
Carrots are a great way to add some color and nutrients to your food. Here are a few recipes:
- Carrot Soup
- Roasted Carrot Spread
- Braised Carrots
- Carrot Halwa
- Carrot Dip
- Carrot Salad
- Gulerodsbrud
- Gulerodsboller
- Carrot Noodles
- Pickled Carrots
- Carrot Cake
FDA regulations
The FDA describes all fresh vegetables, including carrots, as raw agricultural commodities and strictly regulates their growing, harvesting, packing, and storage. This vegetable falls under the 20 most frequently consumed raw vegetables. Canned carrots also fall under the purview of the FDA, which may be sold whole, sliced, quartered, diced, or julienned. The FDA also regulates the use of carrot oil for adding color and flavor to edible products and defines it as the liquid or solid portion of the mixture obtained by the hexane extraction of edible carrots. The USDA regulates the grades of this vegetable and divides them into A, C, and substandard.
References
John Stolarczyk, The History of Carrots, World Carrot Museum
http://www.carrotmuseum.co.uk/history.html
Health Benefits of Carrots, Web MD
https://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/benefits-carrots#1
Ahmad, Tanveer et al. “Phytochemicals in Daucus carota and Their Health Benefits-Review Article.” Foods (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 8,9 424. 19 Sep. 2019, doi:10.3390/foods8090424
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770766/
