
Cinnamon
What is Cinnamon?
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the bark of the Cinnamomum species of trees. It is used as a condiment, flavoring agent, and spice in different cuisines around the world. The spice is sold in the form of curled sticks or ground into powder form. It is brown in color and has a distinctly spicy aroma with a sweet and warm flavor.
- The flavor profile it provides makes it suitable for cooking and baking, and also for desserts such as rice pudding or drinks like Schnapps.
- In some countries, cassia and cinnamon are used as synonyms, however, they are two different spices.
Some of the most popular ground cinnamon brands include:
- Frontier Co-Op
- Simply Organic
- 365
- Burlap & Barrel
- La Flor
- Market Pantry
- McCormick
- Morton & Bassett
- Pereg
- Spice Classics
- Spice Garden
- Spice Hunter
- Trader Joe’s
- Thrive Market
- Wild Harvest
- Whole Foods Market
Origin of cinnamon
This spice is native to Sri Lanka, India, and Myanmar and has been cultivated for over 3,000 years. As a spice, it was extremely valuable in many parts of the world and was one of the first spices to be internationally traded. Arabs had a monopoly on the trade of this spice from South Asia to the rest of the world and to maintain this monopoly, they concocted stories that kept others away from discovering the source.
Culturally, it was also very important, as Ancient Egyptians used it for embalming and in religious festivals. The spice was brought to Europe through Venetian traders and Medieval Europeans used this spice in religious rites as well. When the Portuguese colonized Sri Lanka, the Dutch East India Company later created a monopoly over this spice. Today, cinnamon is grown in many countries around the world.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for cinnamon (1 tbsp, ground):
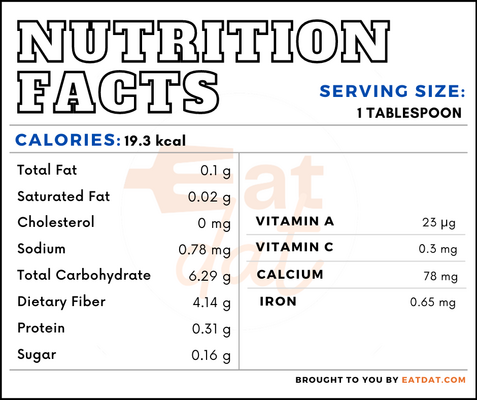
This spice is rich in potassium, carotene, cryptoxanthin, vitamin A, and lutein + zeaxanthin. Also, it contains magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, manganese, choline, vitamin A, lycopene, tocopherol, and vitamin K in decent quantities. Furthermore, this spice has antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption may help combat diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases as well as neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.
Commercial production
The main producers of this spice are Indonesia, China, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, Timor-Leste, Grenada, Sao Tome and Principe, Dominica, and the Seychelles. 50 percent of the world’s cinnamon is consumed by Indonesia, China, the USA, and India, collectively. Cinnamon requires a hot and humid climate, and grows well in all types of soils.
This spice should be stored in a sealed jar or packet and kept away from moisture. Cinnamon sticks tend to hold their aroma and flavor for longer than ground varieties. While the ground version lasts for about a year, the sticks can remain fresh for up to 4 years.
Cinnamon recipes
This spice has a variety of uses and functions in the kitchen. Here are some recipes to try:
- Cinnamon Rolls
- Spekkuk Bumbu
- Beef Rendang
- Coconut Chicken Curry
- French Toast
- Franzbrötchen
- Sugar Biscotti
- Jollof Rice
- Pannekoek
- Bulka
- Lamb Tagine
- Salep
- Vegetable Pulao
- Mangshor Jhol
- Encanelado
- Sopaipillas
- Churros
FDA regulations
Cinnamon falls under the spices, seasonings, and colorings category of the FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations. It is classified as a spice, which is defined as any aromatic vegetable substance in whole, broken, or ground form, whose function in food is seasoning rather than nutritional.
References
Rao, Pasupuleti Visweswara, and Siew Hua Gan. “Cinnamon: a multifaceted medicinal plant.” Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM vol. 2014 (2014): 642942. doi:10.1155/2014/642942, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4003790/
Cinnamon, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), National Institute of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cinnamon
Cinnamon Farming: Planting, Care, Harvesting Guide, Agri Farming, https://www.agrifarming.in/cinnamon-farming-information
