
Cucumber
What is a Cucumber?
Cucumber is a member of the Cucurbitaceae family. It is a type of vine that is widely grown and produces fruits, which are considered as vegetables in popular culture, though botanically considered fruits. Most varieties of cucumber have an elongated shape. The skin may be light green, dark green, or yellow in color, and the flesh is pale green to white.
- While the flesh has a refreshing sweet and mild flavor, the skin has an earthy flavor with bitter undertones.
- The name of the vegetable comes from the belief that it was only fit for cattle consumption, aka, ‘cowcumber’.
Origin
Cucumbers originated on the Indian subcontinent, and there is archaeological evidence pointing towards their existence around 9750 BCE. Later, this fruit spread to China around 2,000 years ago and then throughout Asia. There are references to cucumbers in the Gilgamesh, Bible, and Ancient Egyptian records, as well as records from Ancient Rome and Ancient Greece. By the 9th century AD, this food was already prevalent in France and by the 14th century AD, in England. Colonization spread to North America in the 16th century. By 1880, hybrid varieties began to be produced.
Commercial production
The main cucumber producing countries are China, Turkey, Iran, Russia, Ukraine, the USA, Spain, Mexico, Egypt, and Japan. More than 70 percent of the world’s production comes from China. These fruits grow well in wet and cool climates. They are best suited to sandy loamy soils with good drainage. After 50 to 70 days from sowing, the fruits are ready for harvesting. This must be done around 8 to 10 days after flowering in order to prevent the fruit from becoming bitter.
They are usually consumed fresh but may be stored in the refrigerator for up to three days.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for cucumber (1 pc, raw):
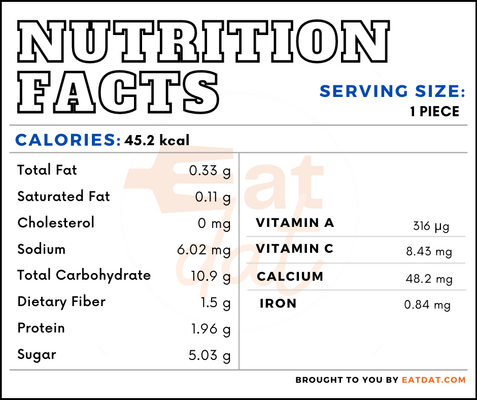
These vegetables are rich in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, vitamin C, folate, choline, carotene, vitamin A, cryptoxanthin, lutein + zeaxanthin, and vitamin K. This fruit has properties that help in reducing the risk of obesity and diabetes. Also, it contains antioxidants, flavonoids, and tannins. Regular consumption may help in improving the skin and preventing constipation.
Cucumber recipes
These vegetables are most often eaten raw in sauces, as snacks, or in salads like Greek salad. They may be pickled in vinegar or brine. Yogurt-based sauces using this fruit, such as raita or tzatziki, are also popular. When sliced, they can be put into sandwiches or cocktails like the Gimlet. Also, they are cooked and used in a variety of dishes. Here are a few recipes:
- Kachumber
- Raita
- Kootu
- Kerabu Timun
- Acar
- Cold Cucumber Soup
- Khyar bi Laban
- Tabbouleh
- Mizeria
- Agua Fresca
- Ice Cream
- Cucumber Collins
FDA regulations
The FDA describes all fresh vegetables, including cucumber, as raw agricultural commodities and strictly regulates all aspects of their growing, harvesting, packing, and storage. Additionally, it counts it among the 20 most frequently consumed raw vegetables. The USDA regulates the grades of these vegetables and separates them into U.S. Fancy, U.S. Extra No. 1, U.S. No. 1, U.S. No. 1 Small, U.S. No. 1 Large, and U.S. No. 2.
References
Elsa Sánchez (professor of horticultural systems management); Francesco De Gioia (assistant professor of vegetable crop science); Lynn F. Kime (senior extension associate); and Jayson K. Harper (professor of agricultural economics), Cucumber Production, Penn State College of Agricultural Sciences, https://extension.psu.edu/cucumber-production
Allie Faden, Cucumber: An Origin Story, Positively Probiotic
https://positivelyprobiotic.com/the-bacteria-blog/cucumber-an-origin-story
Mukherjee, Pulok K et al. “Phytochemical and therapeutic potential of cucumber.” Fitoterapia vol. 84 (2013): 227-36. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.003
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23098877/
