
Flaxseed Oil
also known as Linseed Oil
What is Flaxseed Oil?
Flaxseed oil is obtained from ripened and dried flaxseed. This oil was used by ancient civilizations as a medicinal oil. In modern times, it is used as a cooking oil and may also be used as a dressing oil for salads, soups, and other dishes, in order to improve the taste.
- The oil has a golden yellow color and has a crisp and nutty flavor.
- It has a low smoking point, which means it is not a good choice for fried and roasted dishes.
The top 10 most popular flaxseed oil brands are:
- Zahler
- Nature’s Potent
- Nature Made
- Solgar
- Now Foods
- Jarrow
- 2Healthy
- Puritan’s Pride
- Nature’s Bounty
Origin
Flaxseed is considered to be one of the first crops cultivated by humans. There is archaeological evidence from the Stone Age of humans producing flax for its fiber and seed. It may have originated in the Mediterranean region or India and Ancient Indians, Egyptians, and Chinese used flax extensively for multiple purposes. In addition, it was used as a medicine in India and China. It only spread to the Americas through European colonists.
Commercial production
China is the main flaxseed oil producer in the world, followed by Belgium, the USA, Turkey, Germany, India, and Ethiopia. Flaxseed oil is prepared from the seeds of the flax plant. There are three ways in which this is obtained: hot pressing, cold pressing, and extraction.
Hot pressing involves roasting the seeds and pressing them. The crude oil produced is then filtered and purified. For cold pressed oil, the seeds are pressed at a very low temperature with great mechanical and physical pressure to extract the oil. This is considered the most nutritious oil. The extraction process uses solvent oil in which the seeds are soaked and then the oil is extracted at a high temperature. This oil needs to undergo a refining process before it becomes edible.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for flaxseed oil (1 tbsp):
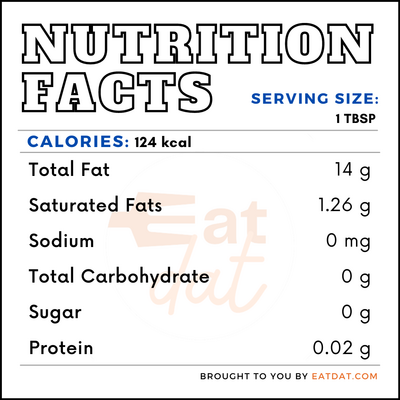
Flaxseed oil is rich in fatty acids and vitamin K. Regular consumption of flaxseed may help in regulating blood pressure, reduces the risk of myocardial infarctions and strokes, assists in keeping diabetes in check, and protects against certain types of cancers, especially breast cancer. The omega-3 fatty acids also helps in brain development and spatial memory as well as protect against menopause symptoms in women. Also, this oil is beneficial for skin health, increasing its hydration and smoothness. It protects against gastrointestinal diseases by giving protection to the gut and inducing healthy bacteria.
However, overconsumption of flaxseed oil may lead to diarrhea or allergic reactions. It is unadvisable for pregnant women in their second or third trimester to consume this oil because of the risk of premature birth. In addition, it is not advised for patients after surgery to prevent the risk of bleeding.
Flaxseed oil recipes
This oil has been used for centuries as a medicine and a food. It is also extensively used in cooking. Here are a few recipes:
FDA regulations
Flaxseed is classified as a grain by the USDA and defined as grain that consists of at least 50 percent of common flaxseed and at most 20 percent of other grains before the removal of dockage, and 50 percent or more of whole flaxseed after the removal of dockage. Additionally, flaxseed oil may be classified as a drying oil for non-culinary purposes.
References
Goyal, Ankit et al. “Flax and flaxseed oil: an ancient medicine & modern functional food.” Journal of food science and technology vol. 51,9 (2014): 1633-53. doi:10.1007/s13197-013-1247-9, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152533/
Linseed Oil Production Technology, ABC Machinery, http://www.bestoilmillplant.com/linseed-oil-production-technology.html
Parikh, Mihir et al. “Dietary Flaxseed as a Strategy for Improving Human Health.” Nutrients vol. 11,5 1171. 25 May. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11051171, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6567199/
