
Hot dog
What is a hot dog?
A hot dog is cured meat shaped in the form of a sausage, that is usually grilled or steamed. The sausage in the sandwich can be a frankfurter or a weiner. These sausages are usually eaten in a bun with different toppings that differ depending on the region where they’re consumed. Toppings can include mustard, ketchup, pickle relish, chili, fried onions, sauerkraut, jalapeños, and more.
- In the US, this dish is synonymous with outdoor sports and summertime grilling.
- In 2019, Americans spent over $6.2 billion on store-bought hot dogs and sausages.
The top 10 hot dogs in the US according to Advance Local are:
- Costco’s Kirkland Beef Hot Dogs
- Nathan’s Angus Beef Franks
- Oscar Mayer Classic Beef Uncured Franks
- Trader Joe’s Uncured Beef Hot Dogs
- Wellshire Sugar-Free All-Natural Uncured Beef Franks
- Whole Foods 365 Uncured Beef Hot Dogs
- Open Nature Uncured Beef Franks
- Roseda Farm Beef Franks
- Safeway Signature Select Beef Franks Scor
- Ball Park Beef Hotdog
Origin
Homer’s The Odyssey mentions sausages as far back at 850 BC. However, historians see Roman times, under the rule of the emperor Nero, as the origin of the sausage. Nero’s cook, Gaius, pulled out a part of a pig’s intestine then filled with wheat, meat, and spices to make a sausage. In the 15th century, a man named Johannes Georghehner invented the frankfurter which would become a staple in German cuisine. In the 19th century, German immigrants popularized sausages in the US by selling them in street food carts.
The hot dog was born when, instead of serving a hot sausage with gloves, a street vendor served a sausage in a bun. Hot dogs soared in popularity due to Nathan Handwerker, who worked at a hot dog stand on Coney Island in 1915. Once Handwerker saved up enough money, he made his own stand and won the competition over by reducing his prices. By the time, the Great Depression rolled around, Handwerker’s hot dogs had already become an American favorite. From picnics to parties to royal visits, this sausage sandwich had earned its place in the American kitchen and culture.
Nutrition
Hot dogs provide protein and vitamin B12 which are vital nutrients for the human body. Nonetheless, they are often criticized for their fat and sodium content. Today, most brands offer low fat or reduced-sodium hot dogs. Combined with diet and exercise, this sausage sandwich can be consumed in moderation.
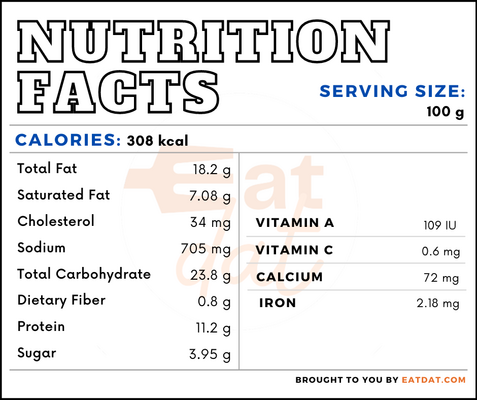
A 100g serving of hotdogs can give you:
Commercial production
When commercially produced, hot dogs are made from a special selection of meat. Often, these meats are pork and beef that are cut into small pieces and placed in a mixer. The meat is then mixed with spices and curing ingredients before being weighed and stuffed into a linker machine. After they are in their casings, the hot dogs move to the smokehouse where they are smoked, cooked, and cooled down. Once cooled, the hot dogs are packaged and vacuum-sealed to protect the freshness of the hot dogs.
Uses
The United States Department of Agriculture recommends following basic food safety guidelines for perishable products to avoid foodborne illnesses. Store-bought hot dogs should be refrigerated as soon as possible and never left at room temperature for too long. In the refrigerator, hot dogs can safely be stored for two weeks, if unopened. Should their packaging be opened, storage time reduces to one week. Hot dogs should only be kept in the freezer for 1-2 months.
Recipes
Ideal for summer barbecues and outdoor events, the hot dog’s versatility knows no bounds. Here are a few popular recipes:
References
Douglas, Charles William. “A Joint American Tradition: Hot Dogs, FDA & USDA.” A Joint American Tradition: Hot Dogs, FDA, & USDA, Harvard Law School, 20 Mar. 2006, dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/8889488/Charles06.html?sequence=2.
Butler, Stephanie. “Break Out the Buns: The History of the Hot Dog.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 28 Aug. 2013, www.history.com/news/break-out-the-buns-the-history-of-the-hot-dog.
Stradley, Linda. “History and Legends of Hot Dogs.” What’s Cooking America, Whatscookingamerica.net, 27 Aug. 2016, whatscookingamerica.net/History/HotDog/HDHistory.htm.
“Hot Dogs and Food Safety.” Usda.gov, United States Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service, https://www.fsis.usda.gov/wps/wcm/connect/6862410d-e659-41ee-82c7-6eae60708c11/Hot_Dogs_and_Food_Safety.pdf?MOD=AJPERES
