
Nutmeg
What is Nutmeg?
Nutmeg is a spice made from the fruit that grows from the Myristica fragrans tree. This tree is native to Indonesia and produces both nutmeg and mace.
Some popular ways to use nutmeg in the kitchen are:
- Spiced Bundt Cake
- Candied Pecans
- Wassail Punch
- Pumpkin Pie
- Spiced Rum
Until the 19th century, the Spice Islands were the only place on Earth that produced this spice. This spice is known for its autumnal taste, as well as its use in meats and savory sauces. In 2018, the worldwide production of nutmeg totaled 109, 284 tons.
Origin of nutmeg
This spice has its origins in Molucca, specifically on the Banda Islands, and was initially traded by the Arabs. After the Crusades, this medical spice made its way to Europe as early as the 12th century. The growing popularity of the spice made the Banda Islands a destination for Portuguese and Spanish traders. By 1512, these travelers finally discovered the location of the famous Spice Islands. In the 1500s, nutmeg became a popular treatment for the plague and was well-known for its hallucinogenic properties.
However, the spice trade would lead to much bloodshed and war between European countries. In the 1600s, the Dutch and British were constantly combatting each other for who would reign supreme over the spice trade. Later in 1677, the Dutch would trade Manhattan to the British for control over one of these islands as it produced nutmeg. The Dutch would later claim all of these islands by the 1880s but leave the Bandanese people to produce the spices they depended on. Nowadays, this spice remains popular and can be found in anything from cola to eggnog to pies.
Function
This can bring a warm, spicy aroma and flavor to any dish. You can use it in both sweet and savory recipes. Sprinkle some of this spice into sweets like cake, puddings, or tarts. Alternatively, you can use it to give flavor to bechamel or ragù sauce.
Nutrition
One teaspoon (2.2g) of nutmeg contains:
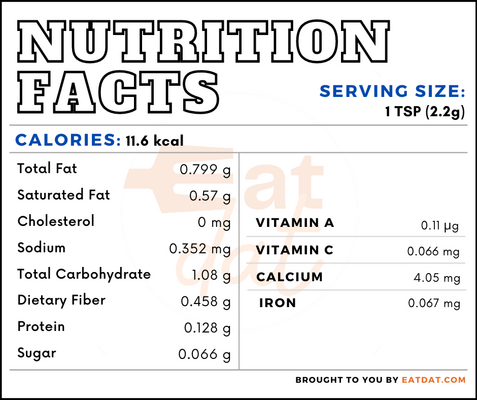
Whether you’re using the whole nut or the ground spice, you’ll rejoice in the health benefits nutmeg provides. Packed full of antioxidants, this spice can help prevent cellular damage, as well as protect against free radicals. Nutmeg also has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Studies have shown that it can even help boost your mood, improve blood sugar control, and keep your heart healthy. However, this spice should be consumed in moderation as consuming it in excess may cause loss of muscle coordination and hallucinations.
Commercial production
The commercial production of this spice begins with planting the seeds, which produce a tree that yields three times each season. Once the tree grows and produces nutmeg, the plant is harvested and has its hard husks removed. Underneath the hard husk, there is a thin red layer of plant matter known as mace, which must also be removed. After that, the remaining kernel is dried in the sun for up to a few weeks. The kernel can be sold on its own or sent off for further processing to become ground nutmeg.
Use
This fragrant spice can bring a world of flavor to many dishes. Although to enjoy it thoroughly, you have to store it properly. To maintain its full flavor, you should keep it in an airtight container away from heat, light, and moisture. If ground, this spice will maintain its freshness for about 6 months. If whole, nutmeg can stay fresh indefinitely when stored correctly.
Nutmeg recipes
This spice helps round out the flavor in a variety of dishes. Here are some popular recipes:
- Lebkuchen – German Gingerbread
- Ragù alla Bolognese
- Nutmeg Cake
- Eggnog
- Spiced Madeleines
- Roasted Carrots
- American Pumpkin Pie
FDA Regulation
The Food & Drug administration includes this spice on its list of natural seasonings and flavorings that are considered safe for consumption. The FDA also has a regulation that describes the quality of whole or ground nutmeg that would call for its seizure. This includes insect infestation, animal contamination, as well as moldiness, or fungal deterioration.
References
“Nutmeg and Mace.” Spices Exotic Flavors & Medicines, UCLA Louise M. Darling Biomedical Library, unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?displayID=19.
Hay, Mark. “The Hidden History of the Nutmeg Island That Was Traded for Manhattan.” Atlasobscura.com, Atlas Obscura, 4 Mar. 2019, www.atlasobscura.com/articles/island-traded-for-manhattan.
“Nutmeg.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 19 Dec. 2019, www.britannica.com/topic/nutmeg.
“CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21.” Accessdata.fda.gov, U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2019, www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=182.10.
