
Tomato
What is a Tomato?
The tomato is the fruit of the Solanum lucopersium plant. It is botanically classified as a berry but is popularly considered a vegetable. The name itself comes from the Aztec word for tomato, tomati. Consumed both raw and cooked, this vegetable is bright red in color and has a tangy and sweet taste with a strong umami flavor.
- This food ranges in size, depending on the cultivar, and smaller varities are known as cherry tomatoes.
- Though of Central American origin, this food has become an integral part of the cuisine in most cultures.
Some popular ways to use tomatoes in the kitchen include:
- Salad
- Pasta
- Salsa
- Soup
- Ketchup
- Sauce
- Roasted
- Curries
Origin of tomatoes
This fruit originated in South America and have been cultivated since at least 500 BC by the Aztecs. They are an integral part of the South American diet. Spanish conquistadors brought the vegetable back to Europe. Originally, it was a decorative plant and was considered poisonous. It eventually spread through the rest of the world through colonization and trade. By the 18th century, it had become popular in many parts of the world.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for tomato (1 whole Italian tomato):
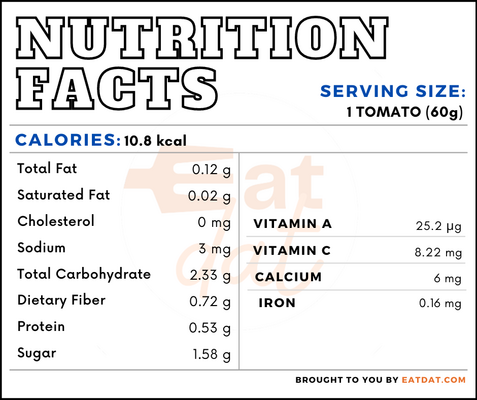
This food is rich in calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, sodium, vitamin C, folate, choline, vitamin A, carotene, lycopene, lutein + zeaxanthin, and vitamin K. Tomatoes contains lycopene, which helps in reducing cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, and mental disorders through its anti-oxidative effects. Also, it has shown some alleviation of menopause symptoms. Furthermore, it helps in increasing vision health, regulates metabolism, and reduces the risk of certain cancers. In addition, this food is rich in antioxidants and polyphenols.
Commercial production
Tomatoes are a warm season crop and require low to medium rainfall. They thrive in sandy loam soils or heavy clay loam soils. When they begin to ripen, they are picked, and then left to fully ripen.
It is best to store tomatoes are room temperature and out of direct sunlight. However, if they are fully ripe, you can keep them in the refrigerator to prolong their shelf life. If they are are unripe, store them at room temperature, stem side down to promote natural ripening for a more flavorful fruit.
Tomato recipes
Tomatoes can liven up any recipe. They are extensively used in preparing salads, soups, curries, pastas, sauces, salsas, dips, juices, and plenty of other dishes. Here are a few recipes to try:
- Pepido
- Hilachas
- Pico de Gallo
- Arroz Rojo
- Pasta Marinara
- Bruschetta
- Tomates Farcies
- Lecsó
- Zupa Pomidorowa
- Matbucha
- Shakshuka
- Loubya
- Thakkali Sadam
- Lagman
- Egg Bhurji
- Dimlama
- Joll of Rice
- Red Red
- Chicken Karahi
- Ayam Masak Merah
- Cá Sốt Cà Chua
- Cà Chua Nhồi Thịt
- Thakkali Curry
- Prawn Rougaille
FDA regulations
Tomatoes fall under the 20 most frequently consumed raw vegetables. In addition, they are classified as a raw agricultural commodity (RAC). Canned tomatoes are defined as the food prepared from tomatoes conforming to the characteristics of the fruit Lycopersicum esculentum P. Mill, of red or reddish varieties. The seeds and stems must be removed, and it may or may not be peeled.
References
Imran, Muhammad et al. “Lycopene as a Natural Antioxidant Used to Prevent Human Health Disorders.” Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 9,8 706. 4 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/antiox9080706, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7464847/
Frusciante, Luigi et al. “Antioxidant nutritional quality of tomato.” Molecular nutrition & food research vol. 51,5 (2007): 609-17. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200600158, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17427261/
Julia Buckley, How this fruit became the star of Italian cooking, Stanley Tucci: Searching for Italy, CNN, https://edition.cnn.com/travel/article/tomato-italy-history/index.html
