
Loquat
also known as Japanese Plum
What is a Loquat?
The loquat, is the fruit of the evergreen tree, Eriobotrya japonica. The fruits grow in clusters and have a mild oval shape. They can be yellow or orange in color with a smooth and tough edible skin and firm but tender flesh. Each fruit contains around five seeds, which are not edible. The fruit has a typical sweet flavor when ripe and has a fruity perfume.
- There are several varieties of this fruit that are cultivated for consumption.
- While they are normally consumed raw, they can also be cooked to provide flavor to different dishes.
Some popular varieties of this fruit include:
- Advance
- Champagne
- Emanuel
- FCN#3
- Gold Nugget
- Golitch
- Juda
- Judith
- MOG20126
- Oliver
Origin of loquat
Loquat is also called Japanese plum, but it actually originated in southeastern China and then spread to other regions and countries. In Ancient China, the fruit was reserved for the royal family and there was a multitude of legends surrounding it. This fruit was introduced to Japan during the Tang dynasty, but there is also some evidence that they grew wildly in the country long before. By the 1700s, they had been introduced to the Mediterranean region and parts of western Europe.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for loquat (1 fruit):
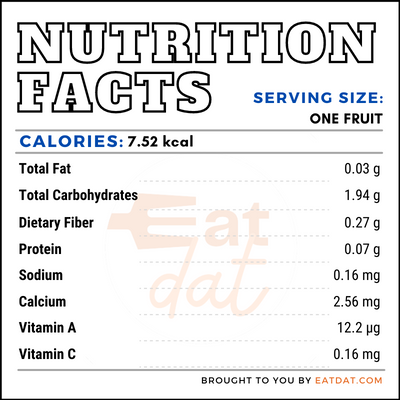
Loquats are highly rich in vitamin A, as well as containing micronutrients such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorous, and folate.
This fruit has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries in order to treat coughs, asthma, and other breathing and lung-related issues. Scientific research has shown that the fruit contains various antioxidants, which help in reducing the risk of inflammation, diabetes, cancers, infections, and allergies. Also, loquats can help in improving the functioning of the liver, lungs, kidneys, and neuronal cells. Regular consumption may prevent obesity, thrombosis, aging, neurogenerative diseases, and cholesterol.
Commercial production
The largest producer of this fruit is China, followed by Spain, Pakistan, Turkey, Japan, Morocco, Italy, Israel, Greece, Brazil, Portugal, Egypt, and Chile. Loquats require a cool climate with distributed rainfall. They thrive in fertile and well-drained, sandy loam soils. Once planted, the plants start giving fruit after three years and continue fruiting for at least 15 years. They are harvested in bunches and generally give up to 20 kg of fruit per tree.
Loquats can be stored in the refrigerator for up to two weeks.
Loquat recipes
The Japanese plum is generally consumed raw as a fruit, but it is also used in a variety of recipes including cocktails, as well as baked goods and confections like jam. Here are a few recipes:
- Jam
- Chicken
- Yeni Dünya Kebab
- Chinese Loquat Syrup
- Biwa Compote
- Panna
- Potato Loquat Curry
- Chutney
- Smoothie
- Loquat Liqueur
- Upside Down Cake
FDA regulations
The FDA describes all fresh fruits as raw agricultural commodities and strictly regulates all aspects its growing, harvesting, packing, and storage. However, loquats are not specifically mentioned in this list.
References
Sagar, Narashans & Pareek, Sunil & Bhardwaj, Renu & Vyas, Navrishi. (2019). Bioactive Compounds of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) L.). 10.1007/978-3-030-06120-3_10-1, https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Species-and-varieties-of-loquat_tbl1_338055629
Nagano, Y., Tashiro, H., Nishi, S. et al. Genetic diversity of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) revealed using RAD-Seq SNP markers. Sci Rep 12, 10200 (2022). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-14358-9
Liu, Yilong et al. “Biological Activities of Extracts from Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): A Review.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 17,12 1983. 6 Dec. 2016, doi:10.3390/ijms17121983, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5187783
