
Pecan
What are Pecans?
Pecans are the edible seeds of the hickory tree. They are considered nuts and used as such in culinary terms. The name of the nut comes from the Algonquin language, which also refers to walnuts and hickory nuts with the same word meaning “all nuts requiring a stone to crack”.
The top 10 most popular pecan brands are:
- Planters
- Happy Belly
- Fisher
- Kirkland
- Terrasoul Superfoods
- We Got Nuts
- Pearson Farm
- La Nogalera
- Farm Fresh Nuts
- Whole Foods Market
Origin of pecans
These nuts are native to North America and were widely used by many of the native tribes. They consumed the nuts wild, and even made a popular drink with it called Powcohicora. Spanish colonists were the first to plant orchards for these nuts in Mexico in the 16th century. Later on, the French transported them to the West Indies, where they took root right away. In the 1800s, this crop’s production became widespread throughout the region, and remains the same today.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for pecans (100 g):
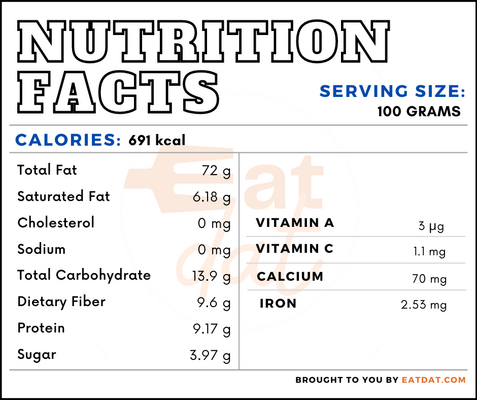
Pecans are rich in micronutrients such as magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and beta-sitosterol. Also, they contain sufficient amounts of calcium, fluoride, folate, choline, carotene, vitamin A, lutein + zeaxanthin, tocopherol, and fatty acids. The nuts are a highly nutritious food that help in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and breast cancer, and in increasing mortality. They assist in reducing LDL and have the property of increasing bioavailability of other foods.
Commercial production
The USA is the largest producer of this nut, accounting for about 75 percent of the world’s production. Other major producers are Mexico, Australia, Israel, Peru, and South Africa.
Pecan trees require three to four years to start producing fruit, but full production only begins at six to eight years. The trees require a deep and well-drained soil, and alluvial river beds are the best for growing them. Their harvesting is done at a crucial time just before germination but after the kernel matures.
When shelled, these nuts must be stored in airtight containers in the refrigerator for up to six months. Unshelled varieties will stay fresh at room temperature for the same period. The high fat content of these nuts can easily make them rancid, so it is best to not keep them at room temperature, especially if shelled.
Pecan recipes
These must be shelled before consumption, and may be consumed raw or roasted with salt, sugar, or spices. Additionally, they work well as garnishes for a variety of dishes including soups, stir-fries, gratins, and salads. Baked goods and desserts containing this nut are very popular. Ice cream, chocolates, and other confectionery also use it as a topping or add-in. Here are a few recipes to try:
- Butter Cookies
- Shortbread Squares
- Candied Pecans
- Pecan Cobbler
- Pie
- Blue Cheese Nut Tart
- Sweet Potato Casserole
- Spaghetti with Pecan Pesto
- Rice Pilaf
- Hot Chocolate
- Cream of Pecan Soup
FDA regulations
The USDA sets the grades and standards for pecan production and distribution. Also, these nuts can be sold as part of mixed nuts, which are regulated by the FDA as requiring at least four or more different types of nuts in a single package.
References
AZ1400, May 2006, Pecan Production Guidelines For Small Orchards And Home Yards, Arizona Cooperative Extension, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, The University of Arizona, https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1400.pdf
McKay, Diane L et al. “A Pecan-Rich Diet Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Nutrients vol. 10,3 339. 11 Mar. 2018, doi:10.3390/nu10030339, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5872757/
Hudthagosol, Chatrapa et al. “Pecans acutely increase plasma postprandial antioxidant capacity and catechins and decrease LDL oxidation in humans.” The Journal of nutrition vol. 141,1 (2011): 56-62. doi:10.3945/jn.110.121269, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21106921/
