
Pumpkin
What is Pumpkin?
Pumpkin is a variety of squash that is a member of the melon family. It is a winter vegetable but is classified botanically as a fruit. Native to North America, this vegetable is huge in size and has a deep orange color on the outside. On the inside, the flesh ranges from mild orange to yellow, and contains large seeds in the middle.
- This food has a sweet and earthy flavor and is often used in both spicy and sweet dishes.
- Culturally, it is associated with Halloween in North America and is used to create jack-o’-lanterns.
Some popular dishes around the world using pumpkin are:
- Pampoenkoekies (South Africa)
- Challaw Kadu (Afghanistan)
- Kar’ Assaly (Egypt)
- Canh bi do thit (Vietnam)
- Camarão na moranga (Brazil)
- Olad’i iz tykvy (Russia)
- Pumpkin curry (Malaysia)
- Nhopi (Zimbabwe)
- Kaddu ka Halwa (India)
- Ghapama (Armenia)
- Calabaza en tacha (Mexico)
Origin of Pumpkin
Archaeological discoveries of pumpkin seeds in the Mexican city of Oaxaca suggest that pumpkins most likely originated in Mexico. This crop dates back 7,500 years and its first varieties were small, hard, and bitter. Pumpkins were the first crops ever grown in North America. Today, they are enjoyed the world over. However, in North America they are a largely decorative crop.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for one cup of pumpkin (116 g, raw):
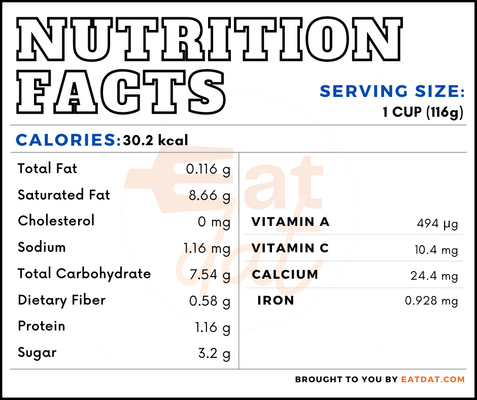
Pumpkin is rich in calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, vitamin C, folate, choline, vitamin A, carotene, and lutein + zeaxanthin. Also, it is a good source of carotene, pectin, as well as other vitamins and minerals. Not to mention, it is rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as lycopene and dietary fiber. The bioactive compounds, including carotenoids, tocopherols, and sterols, available in this food can protect against hypertension, diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. Consumption of this food also helps with digestive problems and acts as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Commercial production
The world’s top pumpkin consuming and producing countries are China, India, Russia, Ukraine, and the USA. Around 26,522,472 tons of pumpkin are produced every year.
As a warm-season crop, it grows best in rich and well-drained soils with mild acidity. It requires plenty of space because the vines like to spread out. However, it must be harvested only when fully mature and the skin has hardened and the color turns deep orange.
This food must be stored in a cool and dry place upside down so that the stalk is at the bottom. It can remain fresh for up to 4 months. Cut vegetables must be stored in a sealed container and kept in the fridge.
Pumpkin Recipes
In North America, pumpkin is usually prepared in the form of pies, although it also popular in soups, bread, or stuffed with different fillings. Due to its sweet flavor, it is also a popular option for preparing smoothies and juices, as well as desserts and baked goods. Additionally, it a popular ingredient for creating autumn ales. Here are a few recipes to try:
- Choctaw Fall Cake
- Spiced Chocolate Cake
- Calabaza en Tacha
- Kürbisbrei
- Kürbiscremesuppe
- Pampoenkoekies
- Miyan Taushe
- Nhopi
- Gr’aa Mderbla
- Flan de Calabaza
- Kaddu ki Sabzi
- Kashi Halwa
- Laksa
- Kolak Waluh
- Tinutian
- Canh Bi Do
- Locro de Zapallo
FDA regulations
The FDA defines pumpkins as an agricultural product which is rarely consumed raw. Therefore, it oversees it growing, harvesting, packing, and holding.
References
Amin, M Ziaul et al. “Comparative study on nutrient contents in the different parts of indigenous and hybrid varieties of pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima Linn.).” Heliyon vol. 5,9 e02462. 13 Sep. 2019, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02462, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6819838/
Pumpkins, The Old Farmer’s Almanac, https://www.almanac.com/plant/pumpkins
Yadav, Mukesh et al. “Medicinal and biological potential of pumpkin: an updated review.” Nutrition research reviews vol. 23,2 (2010): 184-90. doi:10.1017/S0954422410000107, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21110905/
