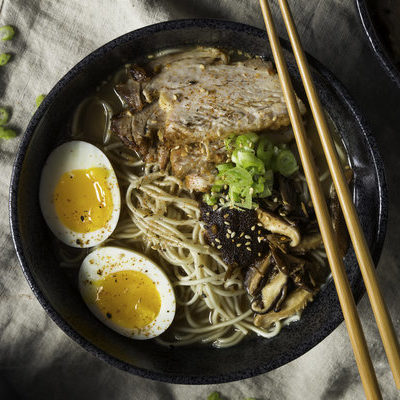

Ramen
What is Ramen?
Ramen is a Japanese noodle soup served with a rich combination of flavorful broth, mix of meats and vegetables, and topped with a boiled egg. This dish is served differently in different parts of Japan. Outside Japan, local ingredients have also made their way into the pot. It is considered a street food in Japan.
- Instant ramen is also very popular throughout the world.
- The top countries consuming these noodles are China, Indonesia, India, Japan, and Vietnam.
The top-selling brands are:
- Maruchan
- Nisin
- Myojo Ippeichan
- Samyang
- Nongshim Shin
- Indomie
- MAMA
- Hao Hao
- Sapporo Ichiban
Origin of ramen
Though the noodle originally comes from China, many countries have adopted it as their own and invented dishes sourced from local ingredients. The exact origin of this soup is unknown but one theory is that it was brought over from China by Shu Shunsui, a Chinese scholar and diplomat. Another theory is that when Japan opened up to the outside world, Chinese travelers took their noodle soup (laa-mein), which was later adapted to become the Japanese ramen. A third theory claims that this was served in Tokyo in the early 1900s in a shop called Rai Rai Ken, which employed Chinese workers.
World War II saw this dish disappear, only to reappear during the post-war boom. Gradually, Japanese travelers and immigrants took ramen to different parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Today, more than a billion packets are sold worldwide each year.
Commercial production
The main ingredients in the noodles are wheat flour, water, salt, and kansui. First, the dough is made by kneading. Then, it is flattened and cut into strips of the desired diameter, steamed, and dipped into a seasoning solution. After, the noodles are air-fried or deep-fried in oil to remove moisture and then cooled before packaging for distribution.
Nutrition
The nutritional value of this dish depends on the ingredients used in preparing it. Broth made from miso can provide vitamins B, E, and K, as well as folic acid. Another popular broth is the pork bone broth, which provides a host of micronutrients, including iron, vitamins A and K, fatty acids, selenium, zinc, manganese, etc. It is also a rich source of collagen. The vegetables added to this provide fiber and a number of micronutrients. The meat provides protein and iron in good quantities. The boiled egg topping provides choline, vitamin D, and antioxidants, in addition to protein and healthy fats.
A 100g serving of ramen noodles contains:
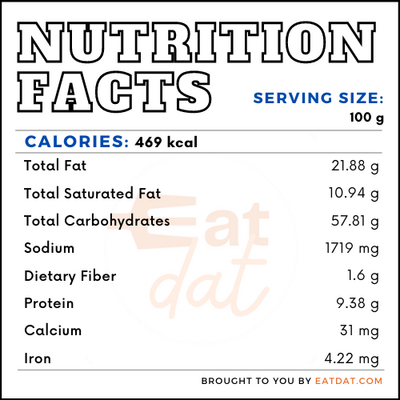
On the other hand, instant ramen may bring health risks in the form of cardiovascular diseases, and increased development of hypertension, obesity, and high blood sugar levels. Instant noodles provide nutrients like thiamine and riboflavin, though they also contain high levels of sodium and unhealthy fats. However, some brands fortify the noodles with micronutrients.
Ramen recipes
This dish can be made in different ways, depending on the broth and toppings used. Here are a few recipes to get you started.
FDA regulations
The FDA classifies all noodles under ‘macaroni and noodle products’. Noodles are defined as any food prepared by drying formed units of dough from any type of wheat flour and eggs, and may or may not include spices, salt, gum gluten, and concentrated glyceryl monostearate. Noodles must have at least 87 percent solid content. The production and sale of instant noodles, including ramen, is governed by the USDA, which specifies that ramen must contain wheat flour. It may also contain vegetable or palm oil, salt, seasoning, sodium phosphates, potato starch, or gums.
References
Carlos Daniel Peralta Rayon, The History of Ramen in Japan, Noodles on the Silk Road,
https://scholarblogs.emory.edu/noodles/2018/07/02/the-history-of-ramen-in-japan-carlos/
Park, Juyeon et al. “A comparison of food and nutrient intake between instant noodle consumers and non-instant noodle consumers in Korean adults.” Nutrition research and practice vol. 5,5 (2011): 443-9. doi:10.4162/nrp.2011.5.5.443
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3221830/
The manufacturing process of instant noodles, World Instant Noodles Association
https://instantnoodles.org/en/noodles/process.html
