
Apricot
What is an Apricot?
An apricot (Prunus Armeniaca) is a small, yellowy-orange fruit of the Rosaceae stone fruit family. This fruit is closely related to peaches, plums, cherries, and almonds.
- Apricots can be consumed raw or cooked, and the fruit is a popular flavor for preserves or jam.
- This fruit has a sweet and tangy taste, although the variety of the fruit determines its skin color.
Some common varieties of this fruit include:
- Chinese Apricot
- Gold Cot
- Tilton
- Wenatchee
- Goldbar
- Gold Kist
- Tomcot
- Autumn Glo Apricot
- Blenheim (Royal)
- Bongo
Origin of apricots
This fruit was cultivated as far back as 2000 B.C. in China and Central Asia. Traders on the Silk Road would transport this fruit to other parts of the globe, such as Persia, where it was known as the yellow plum, or zardaloo. The Persian affinity for this fruit was passed down to the Arabs, and it would remain a common ingredient in the cuisines of Islamic communities. Later on, the fruit traveled to Europe and then was taken to the New World by Spanish colonists in the 18th century. Nowadays, apricots are cultivated in countries all over the world.
Nutrition
A 35g serving of this fruit contains:
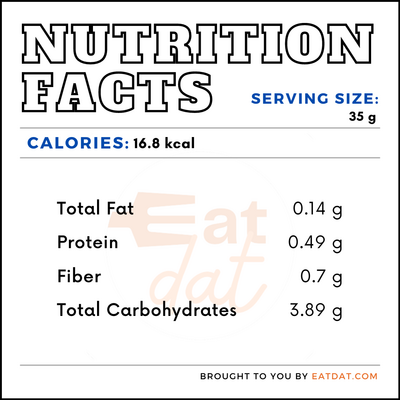
Apricots offer an array of health benefits, due to their antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. The presence of vitamins A & E, as well as beta carotene and carotenoids, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, in this fruit, may help promote eye health. Also, this fruit’s levels of vitamin C have been linked to improving skin health by boosting collagen production and fighting free radicals, which can cause premature aging. Furthermore, the fiber in apricots may aid digestion, prevent constipation, and help regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, the potassium in this stone fruit can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and heart health, as well as reduce the risk of stroke.
Commercial production
The commercial production of this fruit requires specific soil and conditions. First of all, the fruit needs well-drained loamy soil with a pH between 6.5-8.0. Then, the seeds are planted in holes large enough to soak the seed and cover it with soil. It is necessary to soak the apricot seed because it demands more water. Additionally, 3-4 inches of mulch should be added to the base of the plant to keep it free from other vegetation that would cause the fruit to compete for nutrients.
This fruit grows best in a sunny location, as sun aids germination. These trees require pruning and pest control for an optimal yield. It takes between 5-9 months with the proper sun for this fruit to grow. Once the fruits achieve the right size, firmness, and Brix, they are considered mature and ready to harvest. However, these fruits are not harvested when they are fully ripe, as they continue to ripen in storage. Freshly picked apricots are stored in cloth bags to prevent damage, lined into packing crates, and stored until ready for sale.
Apricot recipes
This fruit is well suited to a variety of sweet and savory dishes. Here are some popular recipes:
FDA regulation
The Food & Drug Administration classifies apricots as a raw agricultural commodity. The FDA regulates all aspects of this fruit’s growing, harvesting, packing, and holding. The organization also has a standard of identity for canned apricots, which it defines as food prepared from mature apricots. The regulation goes on to specify which flavorings and spices may be used to produce this canned fruit.
References
“Apricot.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., www.britannica.com/plant/apricot.
Denker, Joel. “’Moon Of The Faith:’ A History Of The Apricot And Its Many Pleasures.” NPR, NPR, 14 June 2016, www.npr.org/sections/thesalt/2016/06/14/481932829/moon-of-the-faith-a-history-of-the-apricot-and-its-many-pleasures?t=1620912970484.
Barrell, Amanda. “Apricot: Health Benefits and Nutritional Value.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/apricot-benefits.
