
Black Pepper
What is Black Pepper?
Black pepper is a spice obtained from the Pieraceae flowering vine. Its fruit, known as peppercorn, is harvested and then dried to make pepper, which is then used in a variety of dishes, including turmeric masala milk, and rendang. Black pepper, green pepper, and white pepper all refer to the same pepper, but in different stages of processing.
- This spice can be used raw, crushed, or powdered in order to season food.
- It is one of the most commonly used spices around the world.
The top 10 most popular brands are:
- The Spice Lab
- McCormick
- Watkins
- Happy Belly Tellicherry
- Soeos Organic
- Viva Doria
- Castle Foods
- Blue Lily Organics
- Melina’s Peppercorns
- McCormick Culinary
Origin of black pepper
Black pepper is native to South India and archaeological evidence shows Indians using pepper at least 4,000 years ago. Trade links between ancient Egypt and ancient India included a robust pepper trade. Ancient Greek and Roman texts refer to the spice, suggesting trade links between India and Europe. Arabian traders controlled the spice route and were successful in introducing pepper to different parts of North Africa, the Middle East, and Mediterranean Europe, where it was prohibitively expensive.
The traders’ wild tales of monsters guarding pepper groves in India protected their trade routes for a few centuries. However, the prohibitive cost of pepper in Europe inspired a new era of explorers who set out to find a spice route to India. Europeans later began to take over the spice trade routes. Today, pepper has a robust trade with 752,000 tons produced around the world.
Nutrition
One tablespoon of ground black pepper contains:
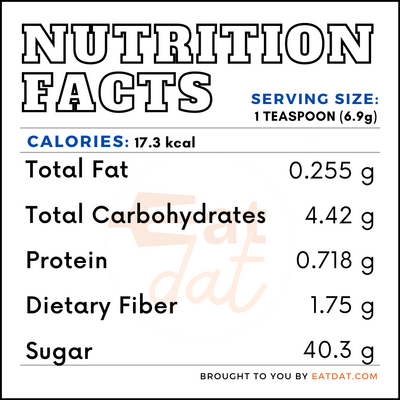
This spice has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. It can help in combating asthma, respiratory diseases, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. It is known for assisting brain function, nutrient absorption, and gastrointestinal function. Also, it has been traditionally used in Indian medicine to treat respiratory tract infection, chronic gut pain, gonorrhoea, menstrual pain, tuberculosis, and arthritis.
Commercial production
Vietnam is the highest producer of pepper, churning 163 thousand tons annually. The other main producers of this spice are Indonesia, India, Brazil, and China. The highest consumers of pepper are Vietnam, India, and the USA, followed by Bulgaria, Indonesia, China, Singapore, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Germany, UAE, and the UK.
Pepper requires a hot and humid climate to thrive, as well as some amount of rainfall. It can be cultivated on different types of soils but well-drained soils with plenty of organic matter are the best for growing pepper. Since black pepper grows on vines, it also requires support to grow. It takes around 6 to 7 months for pepper to grow and be ready for harvesting.
This spice should be stored in tightly sealed containers in a cool and dark place. If exposed to air, they tend to lose aroma and flavor. Whole pepper or peppercorns have a long shelf life, while ground pepper can remain fresh for up to three months.
Black pepper recipes
Pepper is extensively used in different recipes around the world. It is one of the most ubiquitous spices found almost everywhere. Here are a few recipes to try:
- Milagu Pongal
- Pepper Chicken
- Tofu and Mushroom in Black Pepper Sauce
- Thit Kho Tieu
- Shito
- Chocolate Pepper Cookies
- Nasi Goreng
- Cucumber Sandwich
- Peppermelon Cocktail
- Lavender and Black Pepper Cocktail
FDA regulations
Black pepper falls under the spices, seasonings, and colorings category of the FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations. It is classified as a spice, which is defined as any aromatic vegetable substance in whole, broken, or ground form, whose function in food is seasoning rather than nutritional. Oil or other flavorings must not be removed from the product before being sold.
References
Stephanie Butler, Off the Spice Rack: The Story of Pepper, History
https://www.history.com/news/off-the-spice-rack-the-story-of-pepper
Kumar, Sarvesh et al. “Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Piper species: a perspective from screening to molecular mechanisms.” Current topics in medicinal chemistry vol. 15,9 (2015): 886-93. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150220120651
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6295909/
Butt, Masood Sadiq et al. “Black pepper and health claims: a comprehensive treatise.” Critical reviews in food science and nutrition vol. 53,9 (2013): 875-86. doi:10.1080/10408398.2011.571799
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23768180/
Jagdish Reddy, Black Pepper Farming Information Guide, Agri Farming
https://www.agrifarming.in/black-pepper-farming
