
Jalapeño Pepper
also known Huachinango, Chile gordo, Cuaresmeño
What is a Jalapeño Pepper?
The jalapeño pepper is a type of chili pepper and fruit of the Capsicum annus species.
- It has an elongated shape and is commonly available in a green color, though red, yellow, and orange jalapeños are also found.
- Jalapeños have a Scoville unit of between 4,000 to 8,500, which is mild for chilies.
The name itself means ‘from Xalapa’ in Spanish, Xalapa referring to a city in Mexico where it was traditionally cultivated. It is an integral part of Mexican, Tex-Mex, and CaliMex cuisines.
The most popular varieties of chilies from Mexico include:
- Poblano
- Jalapeño
- Pasilla
- Guajillo
- Serrano
- Habanero
Origin of jalepeño pepper
Jalapeños originated in Mexico, where they have been cultivated for several millennia. They were widely cultivated in Xalapa, the capital city of the Veracruz state, though they are no longer commercially cultivated there. The Aztecs were the first civilization to use this chili in their cuisine. Spanish conquistadors spread the usage of jalapeños throughout the world. Nowadays, as Mexican cuisine sweeps across the globe, it is possible to find this pepper almost everywhere.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for jalapeño (1 piece, raw):
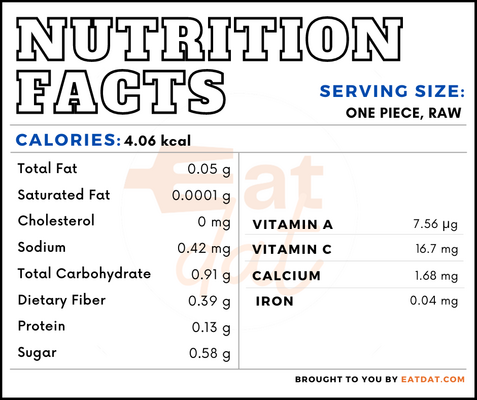
Jalapeño peppers are rich in calcium, folate, choline, vitamin A, carotene, cryptoxanthin, lutein + zeaxanthin, and vitamin K. Generally, chili peppers offer multiple health benefits. Regular consumption may help in decreasing cholesterol and hypertension, increasing absorption of healthy fats (HDL) and satiety, as well as preventing diseases like diabetes, obesity, gastrointestinal diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Also, peppers have antibacterial and anticancer properties, and may help in managing atherosclerosis and metabolic syndrome.
Commercial production
The main chili pepper-producing countries are China, Mexico, Turkey, Indonesia, India, and Spain. Chilies, including jalapeño, require a warm climate and thrive in a mix of humid and dry weather. They grow well in black soil that retains moisture or in sandy loam soil with good drainage. The harvesting is done according to the intended use of the fruits.
Chilies can remain fresh in the refrigerator for up to one month. The rotting is slightly delayed if they are stored with the stalks removed.
Jalapeño pepper recipes
Jalapeño is a mild chili variety that can be used to flavor various dishes and provide some heat to burritos, salsas or fajitas. These peppers are widely used in both North and South America, and even in some Asian countries like Vietnam. Here are a few recipes to try:
- Baked Jalapeño Poppers
- Stuffed Chilies
- Escabeche
- Chiles Toreados
- Beef Enchiladas
- Guacamole
- Mirchi Salan
- Sofrito
- Patatas Bravas Chilenos
- Jalapeño Chimichurri Sauce
FDA regulations
The FDA classifies all chilies under generally recognized as safe category. Also, they are described as a spice.
References
The Jalapeño: A Guide to the Classic Hot Pepper, Sonoran Spice Company Blog, https://blog.sonoranspice.com/jalapeno-peppers-wiki/
Sanati, Setareh et al. “A review of the effects of Capsicum annuum L. and its constituent, capsaicin, in metabolic syndrome.” Iranian journal of basic medical sciences vol. 21,5 (2018): 439-448. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2018.25200.6238, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6000222/
McCarty, Mark F et al. “Capsaicin may have important potential for promoting vascular and metabolic health.” Open heart vol. 2,1 e000262. 17 Jun. 2015, doi:10.1136/openhrt-2015-000262, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4477151/
