
Gooseberry
What is a Gooseberry?
Gooseberry is a type of berry found in a variety of colors, including green, red, orange, purple, yellow, white, or even black. They are slightly larger than grapes in size, and have quite a sour flavor when consumed raw. The berries are mostly used in preparing jams, compotes, sauces, or even in pickling, and can be sweetened or added to dishes for sourness.
Some of the healthiest berries to include in your diet are:
- Cranberry
- Raspberry
- Blueberry
- Blackcurrant
- Chokeberry
- Strawberry
- Goji Berry
- Acai Berry
- Gooseberry
Origin
Gooseberries grew wild in the Caucasian region and in North Africa. They were first cultivated in monasteries in Europe in the 15th century. The name itself comes from the Middle English word ‘groses’, which was derived from the French ‘grosielle’, which meant redcurrant. Gooseberries were recommended as treatment for the plague in the 16th century.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for gooseberry (100 g):
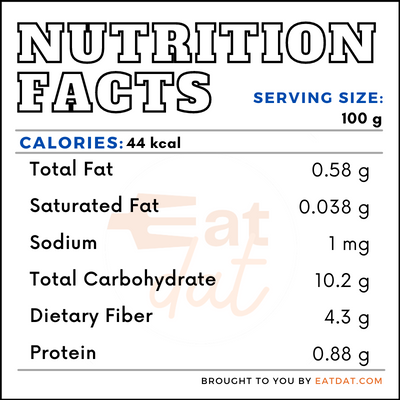
The gooseberry is rich in micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, vitamin C, folate, and vitamin A. Apart from these micronutrients, gooseberries also contain amino acids, phenolic compounds, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and organic acids. Also, they have been proven to reduce oxidative stress. Regular consumption of these berries may help in modulating gut bacteria, as well as reducing the risks of inflammation, certain types of cancers, and diabetes.
Commercial production
The largest producers of gooseberries in the world are Russia, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, Kyrgyzstan, and Moldova.
Gooseberries thrive in loamy soil with neutral acidic and alkaline properties and proper drainage. These plants will have a productive life of around 20 years. The fruit may be harvested before they are ripe or after ripening. These plants must never be planted within 300 meters of white pine trees. Gooseberries were even banned in the US in the early 1990s in order to prevent white pine blister rust that spread through these plants. These berries may be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week.
Gooseberry recipes
Gooseberry is often used to bring a tart flavor to different drinks, desserts, and dishes. Here are a few recipes:
- Gooseberry Cheesecake
- Crumble
- Gooseberry Fool
- Gooseberry Pie
- Clafoutis
- Milk Kisel
- Amla Fry
- Amla Thokku
- Jam
- Nellikai Mor
- Pork Loin
FDA regulations
The FDA describes all berries, including gooseberries, as raw agricultural commodity and strictly regulates all aspects its growing, harvesting, packing, and storage.
References
Gooseberry Production in Manitoba, Agriculture, Province of Manitoba, Canada, https://www.gov.mb.ca/agriculture/crops/crop-management/fruit-crops/print,gooseberry-production.html
Sun, Qing et al. “Ribes himalense as potential source of natural bioactive compounds: Nutritional, phytochemical, and antioxidant properties.” Food science & nutrition vol. 9,6 2968-2984. 3 May. 2021, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2256, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8194758/
Bouyahya, Abdelhakim et al. “Chemical Compounds of Berry-Derived Polyphenols and Their Effects on Gut Microbiota, Inflammation, and Cancer.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 27,10 3286. 20 May. 2022, doi:10.3390/molecules27103286, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9146061/
